When starting a new straightforward web development project, you usually prefer plain HTML, CSS, and JavaScript rather than a front-end framework such as React or Vue. The most familiar step that follows is creating an HTML file and generating a boilerplate.
The code in the boilerplate only includes the essential tags you need for an HTML document. And among these things are meta tags inside the head section of the document. Now, it's usual that you pay little or no attention to these tags. Many developers do not know what they are or their importance.
In this article, you will learn what HTML Meta tags are, their importance to a web page, and how to use them in your HTML Markup. You will also learn which meta tags to prioritize in your Markup and why.
Prerequisites
For you to follow along in this tutorial, you only need the knowledge of HTML Basics.
What are HTML Meta Tags?
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide metadata about your HTML document. Metadata is data that describes other data. So, to put it plainly, HTML meta tags provide information about your HTML document or web page.
The information that meta tags provide is mainly for browsers such as Chrome and Safari and Search engines such as Google and Bing. Browsers and Search engines use this information to understand the content on your web page.
The information in meta tags is not visible to the website's visitors. To include meta tags in your web page, you need to place them between the opening and closing head tags in the Markup. Meta tags are void elements by nature.
Below is an HTML boilerplate generated using Emmet.
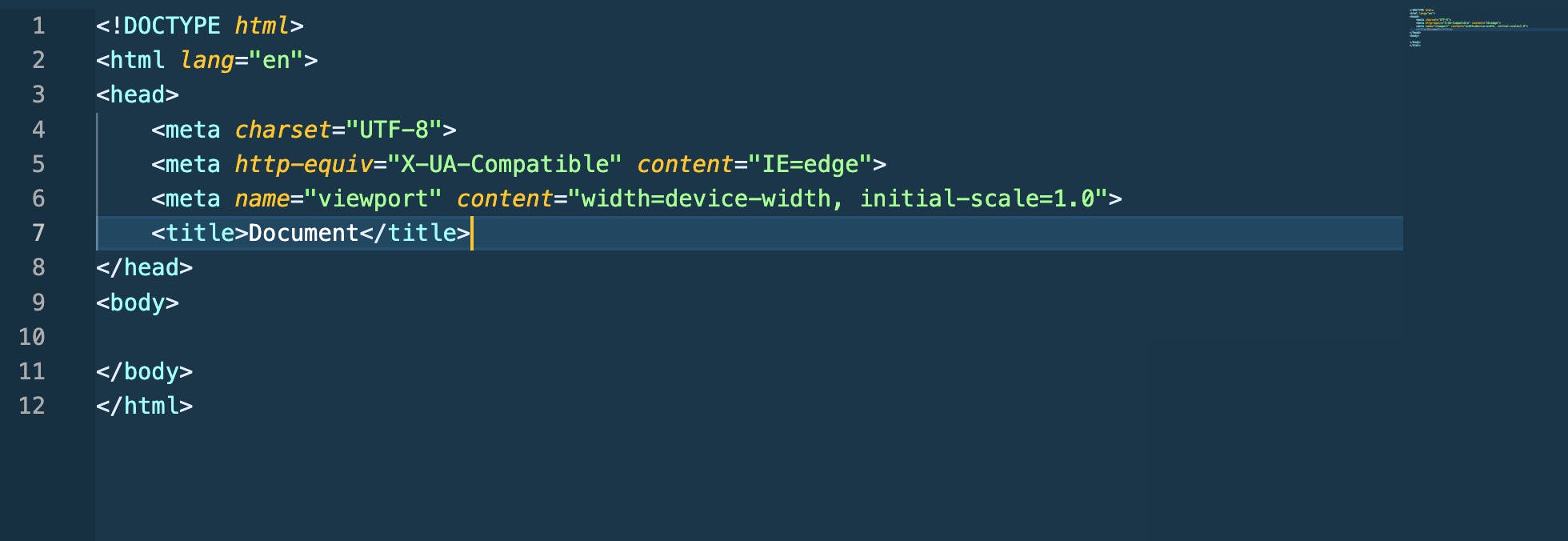
A void element is an element in HTML that cannot have any child nodes (i.e., nested elements or text nodes). Void elements only have a start tag; end tags must not be specified for void elements. (Source: MDN Web Docs)
HTML meta tags convey information by use of attributes. This is where you put the information you want them to bear.
Examples of HTML Meta Tags
Below are some of the meta tags in HTML.
Viewport meta tag
Charset meta tag
Author meta tag
Description meta tag
HTML Meta-related Elements
There are HTML elements that represent metadata but are not metatags. These elements include:
Title tag -
<title></title>Style tag -
<style></style>Script tag -
<script></script>Link tag -
<link>Base tag -
<base>
Meta tags carry metadata that cannot be represented by the above HTML Meta-related elements.
Attributes Accepted By Meta Tags
As mentioned earlier, meta tags use attributes to convey information and can take in any global one. However, they are most associated with the following four:
name
The name attribute provides information that relates or applies to the entire HTML document. You use it with the content attribute in terms of name-value pairs.
The name attribute gives the metadata name, while the content attribute gives its value.
content
The content attribute provides the value for the metadata of the name or http-equiv attributes.
http-equiv
The full name for this attribute is http-equivalent.
This is because all the allowed values are names of particular HTTP headers. (Source:MDN Web Docs)
The values it takes include content-security-policy, content-type, default-style, and refresh.
charset
The charset sets the character encoding of the HTML document. It usually takes in the value utf-8 because it is currently the only valid character encoding for HTML5 documents.
Advantages Of HTML Meta Tags
HTML meta tags have tons of benefits for your web page. Let's take a look at some of them.
Meta tags can improve the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) ranking of your website by providing search engines with more information about your website's content, layout, and target.
Open Graph meta tags can improve social sharing by supplying valuable descriptive media information about the web page's content.
You can use meta tags to specify how different browsers should render your web pages, which ensures that your content doesn't break on various devices.
You can use meta tags to protect your web applications from common security vulnerabilities by specifying security-related metadata like content security policies.
Common HTML Meta Tags And Their Uses
Charset Meta Tag
The charset meta tag in HTML defines the character encoding of a web page.
A character set is an encoding to let computers know how to recognize characters such as letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and whitespace. (Source: MDN Web Docs)
A character encoding is a system that maps bytes to text. Character encodings came to be because computers understand only binary data, 1s and 0s.
The charset meta tag tells browsers which character encoding to use for a web page, thus enabling text to be displayed correctly even on different devices.
If a web page renders with the wrong character encoding, it might produce broken characters that we refer to as Mojibake.

Format of a charset meta tag:
<meta charset="character_set_name">
Example:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
</head>
UTF-8 character encoding is used widely for its universal language support.
Author Meta Tag
The author meta tag provides information on the author of a web page, usually the name or social media profile. This meta tag is optional.
Format:
<meta name="author" content="information on author"/>
Example:
<head>
<meta name="author" content="Mbaziira Ronald"/>
</head>
Http-Equiv Meta Tag
The http-equiv meta tag specifies an HTTP-Header for the HTML document. The HTTP-Header provides information to the browser on how to handle the HTML document, for example, the cache settings of the document.
Format:
<meta http-equiv="HTTP-Header-name" content="HTTP-Header-value"/>
Example:
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"/>
Below are some of the header names (on the left) and some of their values (on the right) this meta tag takes in:
Content-type: application/json and image/jpeg.
X-UA-Compatible: IE=edge
Refresh: 5 (Any figure)
Cache-Control: no-cache
X-UA-Compatible header
You will usually see the http-equiv meta tag in the below example among the meta tags when you generate an HTML boilerplate.
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"/>
This particular header name X-UA-Compatible and its value IE=edge specify how the Internet Explorer browser should handle the HTML document. Microsoft laid the browser to rest in 2022.
The header tells internet explorer which version of the browser to use to open the HTML document. The tag tells the browser to use Internet Explorer's latest version to render the HTML document, regardless of the one a user has on his machine.
Around the time of writing this article, Microsoft had laid to rest Internet Explorer, the browser for which this meta tag aims. You can read more about the retirement of Internet Explorer here.
Refresh header
One of the few tricks beginners usually like to play is with the refresh header which specifies after how many seconds the HTML web page should refresh.
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="5">
Let's see this in action ↓
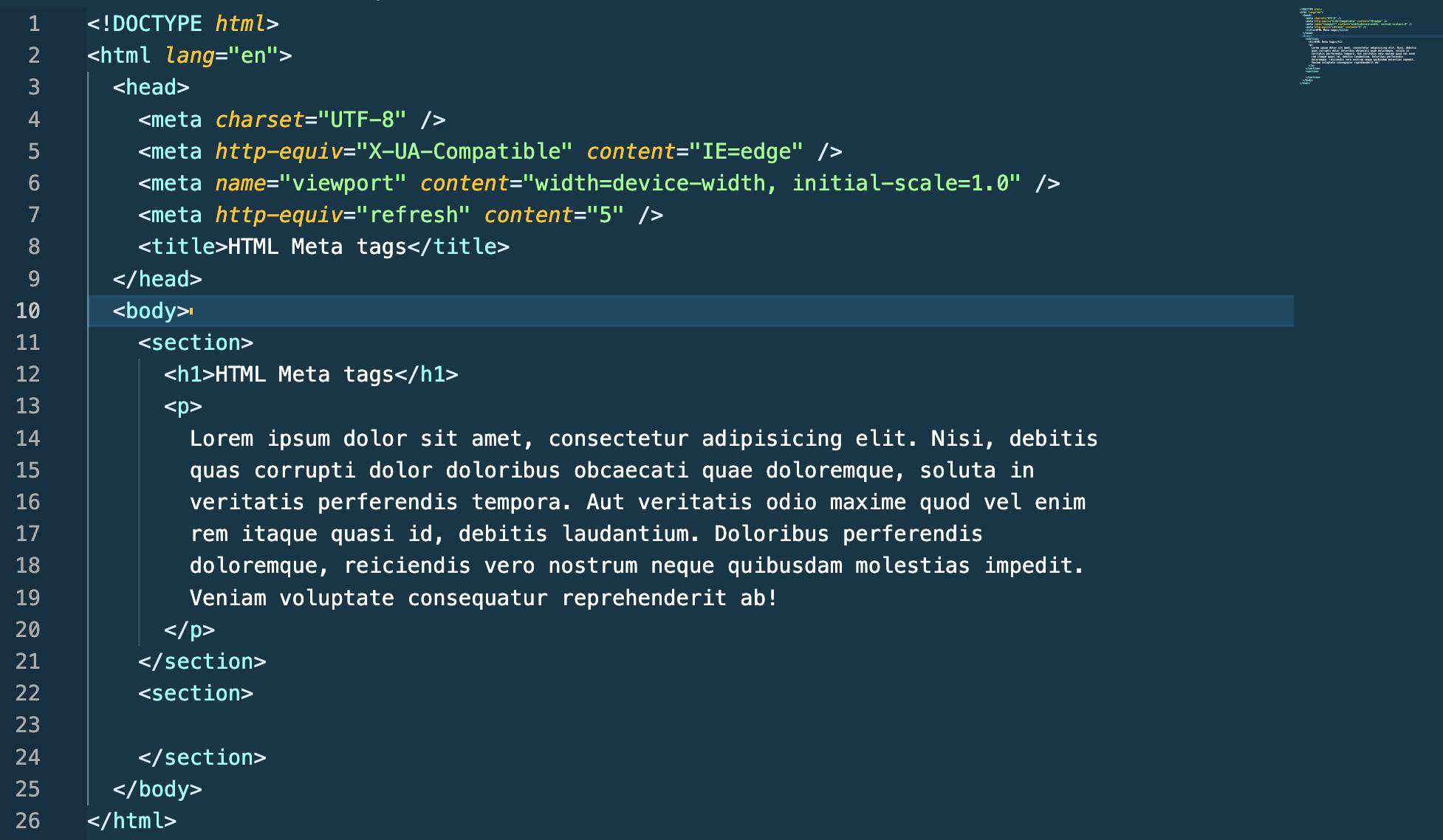
It can also redirect to a specific URL after reloading.
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="6;url=https://twitter.com">
Viewport Meta Tag
The viewport meta tag is one of the most familiar meta tags. It sets the height, width, and zoom levels of the web page's viewport on mobile devices.
A viewport represents a polygonal (normally rectangular) area in computer graphics that is currently being viewed.
In web browser terms, it refers to the part of the document you're viewing which is currently visible in its window (or the screen, if the document is being viewed in full screen mode). (Source:MDN Web Docs)
Format:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
The viewport meta tag is handy for optimizing web pages by specifying height, width, and zoom properties in its content attribute, as most web pages are not mobile screen optimal.
Among the properties it has, let's look at the following in more detail.
Width property
The width property controls the width of the viewport. Typically, developers assign the value of device-width equal to 100vw (viewport width). It ignores negative values.
height property
The height property controls the height of the viewport. It has the value of device-height which is 100% of the viewport height. It also ignores negative values.
initial-scale property
This property controls the zoom level of the viewport when it is first loaded. It has a default value of 1, a minimum value is 0.1, and a maximum of 10.
Description Meta Tag
This meta tag provides a summary of the content on the web page. The summary is usually 160 characters or less. Search engines use this summary as a snippet that shows up in the search results together with the title of the web page.
Format:
<meta name="description" content="Write description of what your web page is about here">
Example:
You can check out this google article on how to create unique descriptions for your web pages.
Open Graph Meta tags
Open Graph meta tags (also known as OG meta tags) control the appearance of a web page when you share the URL on social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn.
Let's take a look at the examples in the images below. The previews are of Hashnode articles, What Exactly Are Sentence Fragments and How To Create Responsive and Customizable UI Components Using Tailwind, shared on Twitter. The noticeable features of the previews are the articles' images, links, titles, and descriptions.
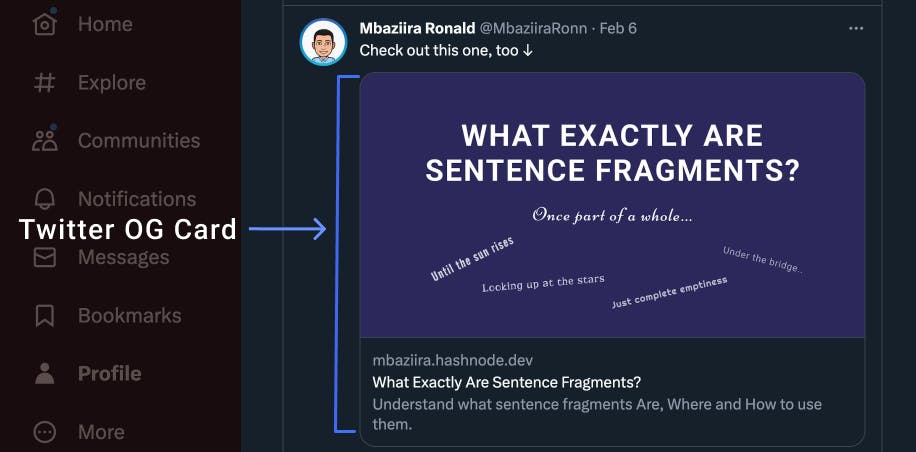
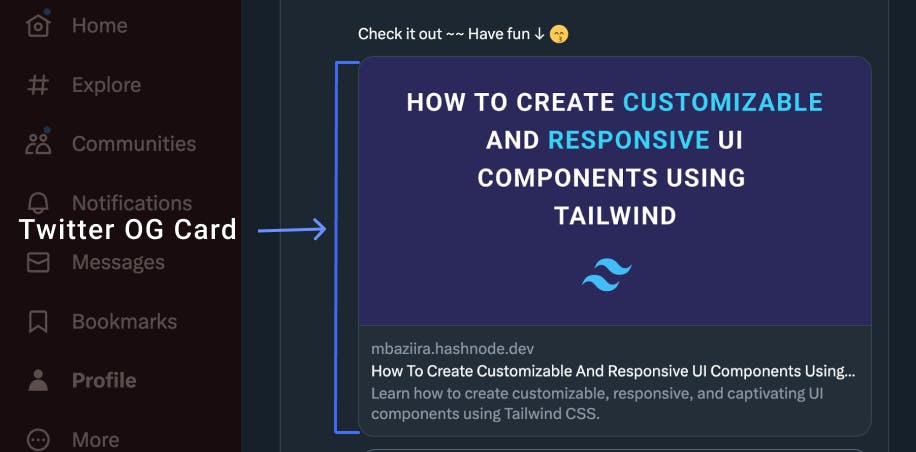
OG meta tags take in the property attribute, which specifies the open graph property related to the content. It is one of the indicators that a meta tag is an Open Graph meta tag. Some properties have extra optional properties that you can use alongside them.
For the above previews to be possible, the OG meta tags use the Open Graph Protocol. The Open Graph Protocol has four expected properties for every web page if you are to use it.
These are:
og:title
og:type
og:image
og:url
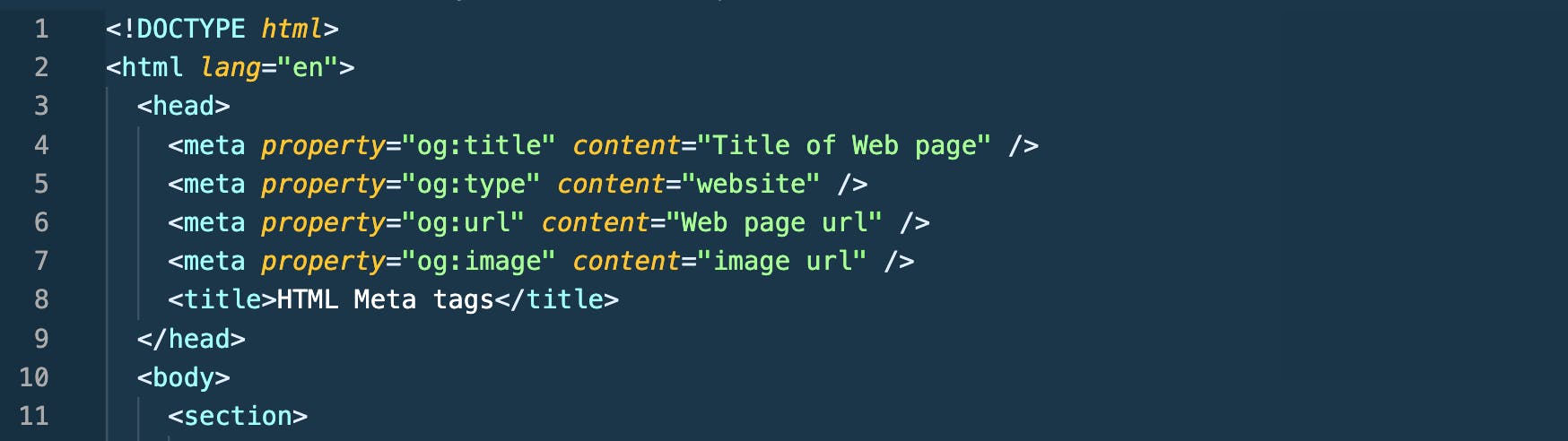
The above OG meta tags would resemble something like in the image below when in the HTML Markup.
"The Open Graph protocol enables any web page to become a rich object in a social graph." (Source: Open Graph Protocol)
Without further ado, let's look at the OG meta tags that make it possible to control the preview or appearance of web pages on social media platforms.
OG Title
The OG Title meta tag specifies the title for the web page to display in the web page preview on social media platforms.
Format:
<meta property="og:title" content="Web page title">
Example:
<meta property="og:title" content="How To Create Responsive And Customizable UI Components Using Tailwind">
The image below shows the OG Title of an article shared on Twitter.

OG Type
The OG Type Meta tag defines the type of content the web page contains. It can take in a couple of types but these are the most common ones:
website
article
music
video
book
It helps social media platforms understand the type of content you are sharing.
Format:
<meta property="og:type" content="type_value" />
Example:
<meta property="og:type" content="article" />
OG Description
The OG Description meta tag provides a summary or brief description of what the web page is about when you share it on social media platforms.
The image below shows the OG Description of an article shared on Twitter.

Format:
<meta property="og:type" content="write og description here">
Example:
<meta property="og:type" content="Learn how to create customizable, responsive, and captivating UI components using Tailwind CSS">
OG Image
The OG image meta tag specifies the image you want to display when you share your web page on social media platforms.
Format:
<meta property="og:image" content="image_url">
Example:
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/ogimage.jpg">
The OG image meta tag can have more properties to which you can attach more metadata. These include:
og:image:width
og:image:height
og:image:alt
Each of these properties is put in its meta tag and not the main one with the property of og:image.
It would be like this:
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/ogimage.jpg"><meta property="og:image:width" content="400" />
<meta property="og:image:height" content="300" />
<meta property="og:image:alt" content="A cover with the title of the article" />
Note:
The og:image:width and og:image:height are in pixels.
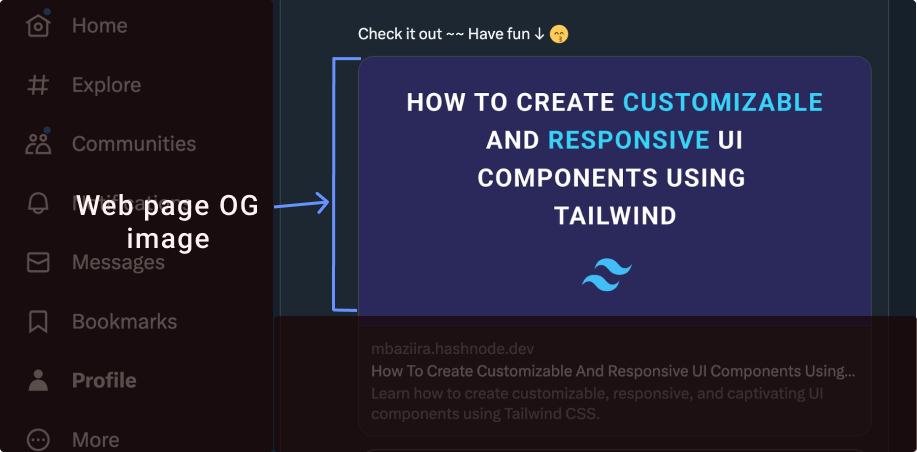
For articles like this or How To Create Customizable and Responsive UI Components Using Tailwind, blogging platforms like Hashnode provide a UI interface where you can upload your OG image.

OG Url
The OG Url meta tag specifies the canonical URL for the web page.
"A canonical URL is the URL of the best representative page from a group of duplicate pages." (Source: Google support)
Why a canonical URL, I hear you ask? Well, it's because pages can have duplicates, and among these, you would like a particular web page URL to be indexed by search engines rather than one of the others such that its ranking is not affected. For articles, it is usually the original post.
Format:
<meta property="og:url" content="canonical URL" />
Example:
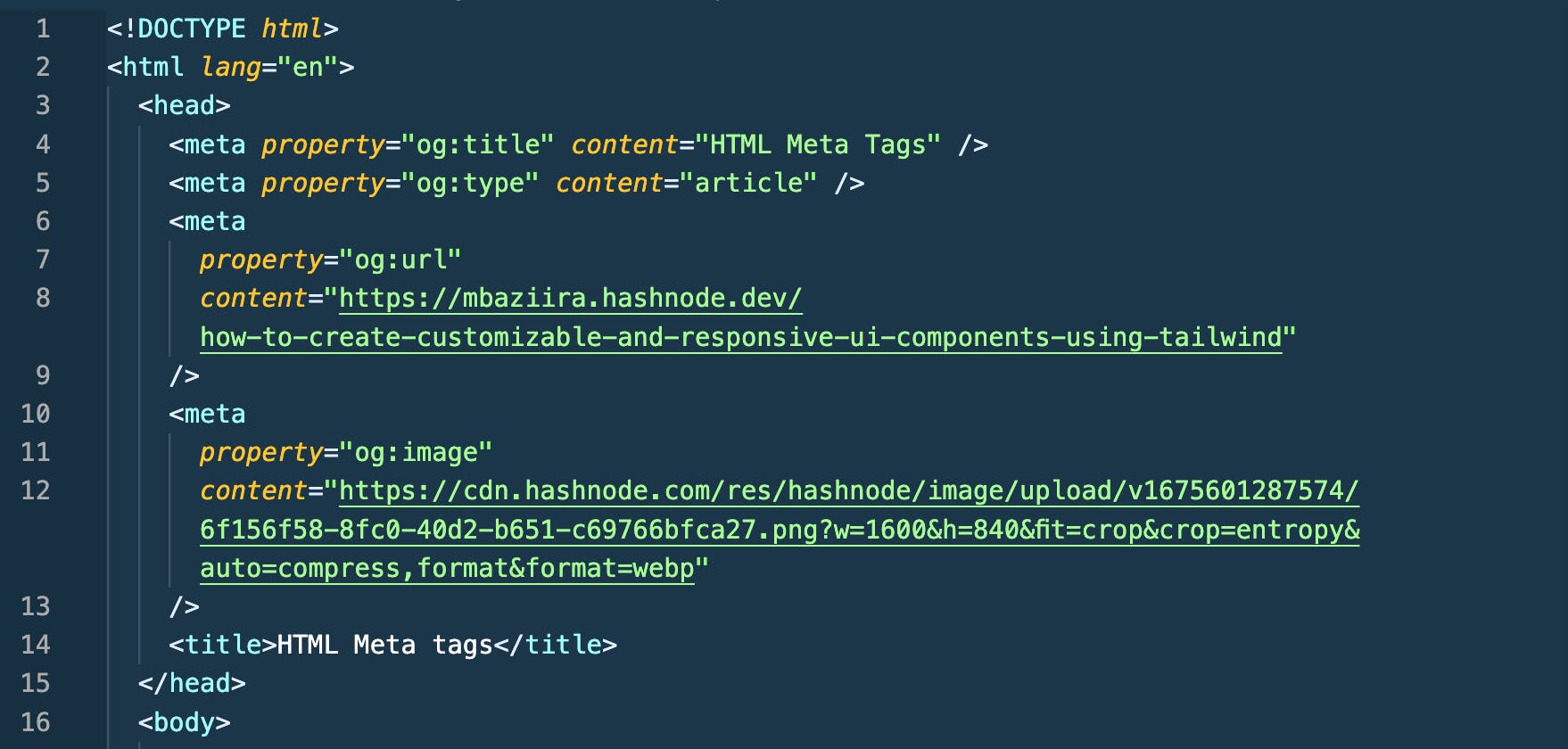
<meta property="og:url" content="https://mbaziira.hashnode.dev/how-to-create-customizable-and-responsive-ui-components-using-tailwind"/>
OG Site name
The OG Site name meta tag indicates the name of the website, brand, or company. This OG site name meta tag is optional.
Format:
<meta property="og:site_name" content="Write site name, company or brand name here">
Example:
<meta property="og:site_name" content="Tweetos">
Conclusion
There are far more advantages and examples of HTML meta tags than the ones you have read about here in the article. I implore you to take the knowledge you have gained to the next level by practicing using meta tags in your Markup.
You will understand the importance of meta tags and how they work much better when you start using them in your project.
For any questions or anything you wish to comment on, kindly leave it in the comments below. Thanks for taking a read. See you soon!
